Construction scheduling is the backbone of any successful construction project.
It not only ensures that tasks are completed in the right sequence but also helps in the efficient allocation of resources and timely completion of the project.
In this guide, we’ll provide an in-depth look at construction scheduling, including different methods, tools, challenges, and best practices.
What is Construction Scheduling?

Construction scheduling is the process of determining, sequencing, and optimizing the tasks and resources needed to complete a construction project within a defined timeframe.
It involves breaking down the entire project into individual activities, estimating their duration, determining dependencies, and scheduling them in a logical sequence.
The schedule serves as a roadmap that visually depicts the flow of the project. It helps coordinate contractors, vendors, and internal teams so work can progress seamlessly. Scheduling enhances efficiency, cost control, and timely delivery – making it invaluable for construction projects.
Key Scheduling Methods
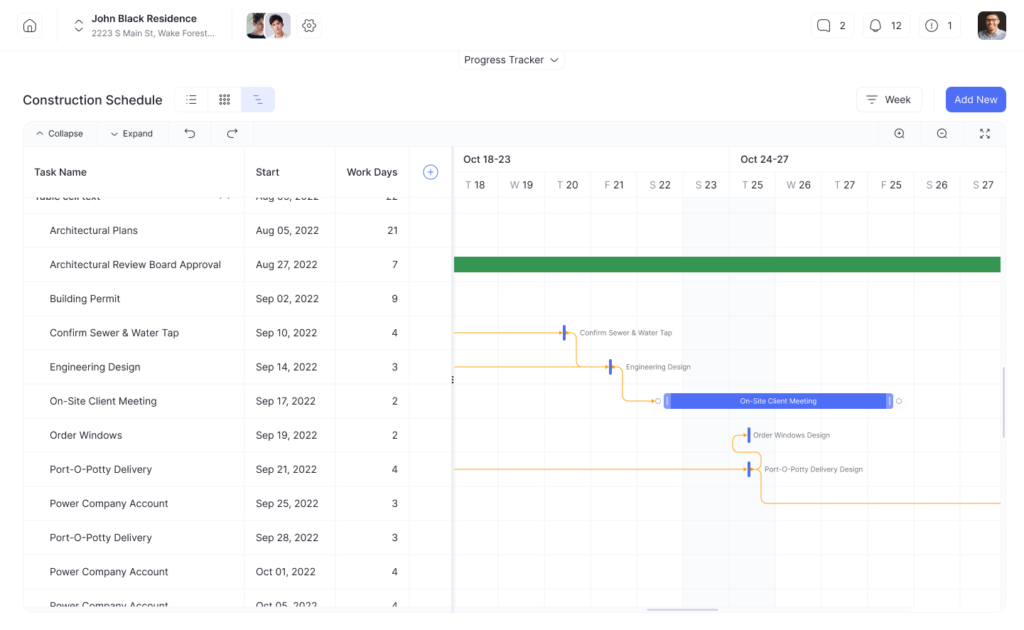
1. Gantt Charts
The most common scheduling method is the Gantt chart. It’s a visual representation of tasks spread across a timeline.
Gantt charts clearly outline task sequences, durations, milestones, and dependencies. They provide a macro view of the project schedule and are great for planning and tracking progress.
BuilderPad allows you to create your construction schedule in the gantt view allowing you to make schedule adjustments quickly with drag and drop simplicity.
2. Critical Path Method (CPM)
For complex projects, CPM is an ideal technique. It identifies the sequence of critical activities that directly impact the project completion date.
By focusing on optimizing the critical path, managers can deliver the project faster. CPM helps assess schedule feasibility and vulnerability.
3. Program Evaluation Review Technique (PERT)
PERT introduces uncertainty into schedule estimates by providing three duration estimates – optimistic, pessimistic, and most likely.
It uses probability distributions to determine timelines, making it more robust than fixed estimates. PERT is best for high-risk projects with variable durations.
4. Line of Balance (LOB)
Ideal for projects with repetitive elements like high-rise apartment buildings, LOB schedules resources to maintain a steady workflow.
LOB tracks productivity rates to identify inconsistencies. It suits large-scale repetitive projects well.
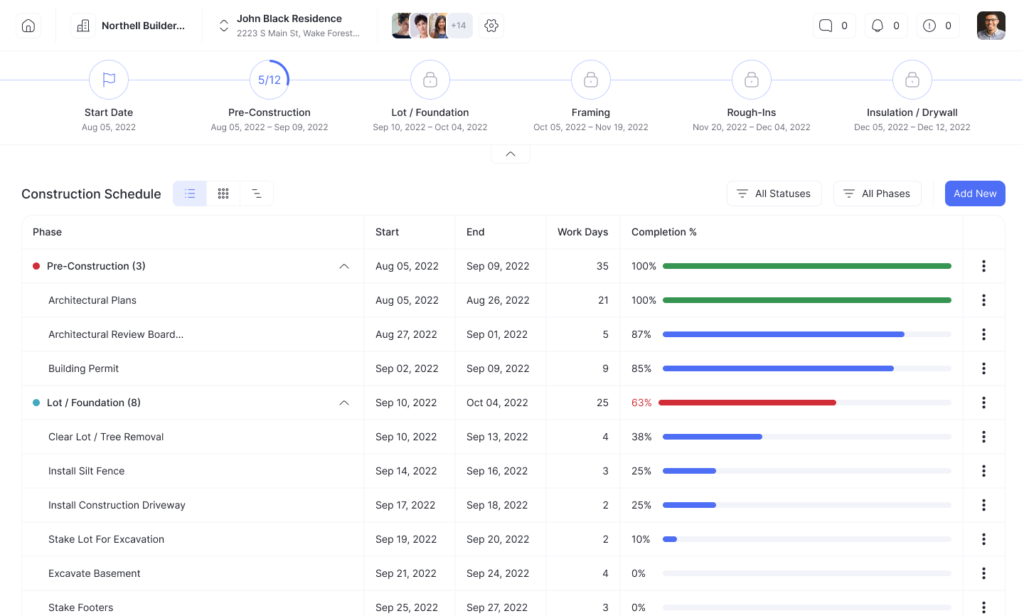
Key Components of a Construction Schedule

1. Tasks/Activities
The building blocks of any schedule are the tasks or activities that must be performed to complete the project, from mobilization to demobilization. Every discrete work item is listed out.
2. Duration
The time required to complete each task is estimated based on historical data, resources assigned, and expert judgment. Padding timelines leads to inaccuracies.
3. Milestones
Important checkpoints like completing the foundation, topping out are marked as milestones. These provide motivation and validate progress.
4. Dependencies
Certain tasks rely on other precedential tasks. Identifying these dependencies ensures a logical flow.
5. Resources
The labor, equipment, materials or services needed for each activity are mapped out. This facilitates resource optimization.
6. Deadlines
Project completion date and interim milestone deadlines are demarcated. Meeting client expectations depends on adhering to deadlines.
Creating a Construction Schedule
List all activities
Granularly define all tasks, from mobilization to post-construction. Break down large activities into smaller work items for better management.
Determine dependencies
Note predecessor and successor relationships between tasks using arrows or matrix formats. This prevents sequence errors.
Estimate durations
Leverage historical data and expert judgment to estimate task durations. Pad sparingly, if at all. Account for resource constraints.
Map resource requirements
Determine the labor, equipment, materials and services needed for each task. Understanding work crews’ composition and site conditions will improve estimates.
Develop schedule
Use scheduling software to develop the baseline schedule with tasks, durations, dependencies and milestones.
Validate and control
Have experts review the schedule for errors. Once approved, monitor progress continually and update the schedule regularly.
Construction Scheduling Challenges
- Dealing with weather delays, permit delays, supply chain, rework, scope changes, and change orders
- Managing slow mobilization, delays in material delivery or equipment failure
- Estimating activity durations accurately with limited data
- Preventing resource conflicts arising from over-allocation
- Maintaining a robust schedule with multiple interdependencies
- Updating master schedule while tracking daily progress
Tips for Effective Scheduling
- Define activities at appropriate detail level
- Use rolling wave planning as details emerge
- Estimate conservatively and pad timelines minimally
- Clearly outline requirements, constraints, assumptions
- Continuously monitor progress and adjust
- Integrate schedules with budgets and contracts
- Leverage CPM, PERT and other techniques appropriately
- Maintain contingency reserves for uncertainties
- Collaborate with contractors, vendors, and inspectors
With a solid understanding of scheduling techniques, vigilance over progress, and proactive risk management, construction managers can develop and maintain schedules that keep projects on track. A schedule provides clarity, coordination, and control – enabling on-time, on-budget delivery of construction projects.
Key Takeaways:
- Construction scheduling is vital for efficiency, cost control, risk mitigation, and on-time delivery of projects.
- Different scheduling techniques like Gantt charts, CPM, PERT, and LOB are suited for different types of projects based on complexity and repetitiveness.
- Accurately estimating task durations, mapping dependencies, and allocating resources are crucial for creating a realistic schedule.
- Scheduling software like Primavera P6 helps develop and manage optimized schedules.
- Updating the master schedule frequently by incorporating actual progress is important to keep projects on track.
- Managing uncertainties, delays, scope changes and resources effectively is key to maintaining robust schedules.
- Integrating the schedule with budgets, contracts and quality metrics improves project control.
- Open communication, collaborative planning, and schedule audits help minimize errors and maximize optimization.
- Construction scheduling is an evolving art and science that project managers should continuously learn and refine through training and experience.
- Leveraging scheduling best practices can make the difference between a successful timely project and one that is delayed or over budget.
In summary, construction scheduling requires breaking down projects into activities, estimating durations, setting milestones, determining dependencies, allocating resources, and continuously monitoring progress against the schedule. Implementing scheduling best practices goes a long way in keeping construction projects on time, on budget, and minimizing risks.







